2. ASM and OCFS are installed into a single Oracle Home called "Grid Infrastructure Home"
3. ASM provides more enhanced feature in 11g, As a part of this, we can now store OCR and voting disk on ASM. This feature provides complete storage solution in 11g.
4. SCAN(Single Client Access Name): SCAN is the virtual host name to provide to all the clients connecting to the cluster. It's basically a domain name registered wither with DNS or GNS.
5. SCAN name is the name of the cluster itself(default value is the name of the local-node in our case as rac1)
6. SCAN must resolve at least 1 ip address for the installation.
7. Most importantly, SCAN must belong to the same subnet as the public and VIP domains.
8. The usefulness of the SCAN is that because it's associated with the cluster itself, we can easily add/remove nodes without needing to reconfigure the clients(Transparent to the client)
9. Grid infrastructure starts the LOCAL LISTENER(All the nodes) to listen on VIP and SCAN Listener on SCAN VIP. That's the reason we create listener with the name LISTENER on the grid Oracle Home while installing RAC database, any other name to it will give an error that it couldn't start the LOCAL LISTENER
10. How SCAN works?
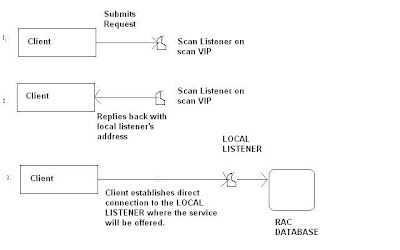
11. The Grid Naming Service (GNS) is a new feature in the 11g R2 Grid Infrastructure . Its design is to simplify the management of the network configuration of the RAC. When GNS is used, it eliminates the manual allocation of the Node and Single Client Access Name (SCAN) Virtual Internet Protocol (VIP) addresses. It also eliminates the need to configure VIP names and SCAN names in a Domain Name Server (DNS) as GNS provides the name resolution for the cluster.
No comments:
Post a Comment